 by adding the measures user and system times, with the
predicted blocking time.
by adding the measures user and system times, with the
predicted blocking time.



Although figure 3 suggests that
the performance of REMOTE_MEMORY is significantly better than
the performance of DISK, the completion time
of an application even under REMOTE_MEMORY
may be unacceptably high.
Hopefully, the performance of REMOTE_MEMORY
will be improved as soon as the Ethernet interconnection network is
substituted with a faster one (e.g. FDDI, ATM, FCS, etc.).
To evaluate the performance of the
applications on top of faster networks, or faster disks we
make detailed performance
measurements that separate
the completion time of the application
into three factors:
(i) bandwidth-dependent blocking time,
(ii) useful user time, and
(iii) protocol-dependent systems overhead.
Using the provided time command we measure the elapsed time
for each application which is the sum of factors (i)-(iii). The
same command also provides the user-time (factor (ii)), and the
system time (factor (iii)).
If from the elapsed time, we subtract
the user plus the system time, we get the time the system was idle
waiting for pages to go through the interconnection network (factor (i)).
By dividing this idle time
with the number of page ins plus page outs, we get the average time
the application waits for each page to go through
the interconnection network. Assuming that an X
times faster interconnection network will reduce this waiting time by
a factor of X, we can predict the
completion time of the application on the faster network  by adding the measures user and system times, with the
predicted blocking time.
by adding the measures user and system times, with the
predicted blocking time.
We made all these measurements on our FFT application, and predict its performance on a system with an interconnection network which is two and ten times as fast as the Ethernet. We also predict its completion time on a system with twice as fast disk ( DISK*2), and on a system that has enough memory to hold all the working set of the application ( ALL_MAIN_MEMORY). The predicted execution times, along with the measured execution times of DISK and REMOTE_MEMORY are plotted in figure 4. We see that ETHERNET*10 performs very close to ALL_MAIN_MEMORY, and significantly better than both REMOTE_MEMORY and DISK.
To understand the results shown in figure 4,
we analyze the execution time of FFT
with 28Mbytes of input. The measured elapsed time is 208 seconds,
consisting of
78.5 sec of useful user time,
5 sec of system time,
and 124 sec of network blocking time,
spent waiting for pages to go through the Ethernet.
During the same run, the application suffered
6520 page-outs and 7791 page-ins.
The average waiting time for a page transfer
(both for page ins and page outs) on top of the Ethernet
is  , or about 8.6 ms. Using a ten times
faster interconnection network, the average waiting time will be reduced
at least to 0.86 ms. Thus, the total completion time of FFT would be
at most
, or about 8.6 ms. Using a ten times
faster interconnection network, the average waiting time will be reduced
at least to 0.86 ms. Thus, the total completion time of FFT would be
at most 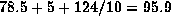 sec,
divided as follows: 82% in user time, 5% in system time, and
13% in network blocking time.
We see that a 100 Mbit/sec interconnection network reduces the total
paging overhead to a mere 17% of the total applications execution time.
We believe that most users would be willing to pay such an overhead
in order to run an application that does not fit in main memory.
sec,
divided as follows: 82% in user time, 5% in system time, and
13% in network blocking time.
We see that a 100 Mbit/sec interconnection network reduces the total
paging overhead to a mere 17% of the total applications execution time.
We believe that most users would be willing to pay such an overhead
in order to run an application that does not fit in main memory.

Figure: Performance of FFT for various Architecture Alternatives.
DISK is the measured completion time when paging to
a local disk.
REMOTE_MEMORY is the measured completion time when paging to
remote memory on top of the Ethernet.
ETHERNET*2 and ETHERNET*10 is the predicted completion time when
using remote memory as a paging device, on top of a network
that is twice and ten times
as fast as the Ethernet interconnection network.
DISK*2 is the predicted completion time when using
a twice as fast disk for paging.
ALL_MAIN_MEMORY is the predicted completion time of FFT
when we use the same workstation but with enough memory to
hold its entire working set.


